AI, KRR, and the Semantic Web
Winter 2019
Instructor: Raghava Mutharaju
IIIT-Delhi

Artificial Intelligence
- It is the study of the general principles of building intelligent agents.
- An agent is any device that can perceive its environment through sensors and react to it by taking action to achieve a stated goal.
- Mimicking human senses, i.e., sight, sound, touch, smell, taste, is a form of perception.
- Intelligent agents should be able to interpret and process other forms of input such as text, semi-structured, and structured data.
- Output of an intelligent agent could be in multiple forms such as movement (reaching a destination), decision taken, sound etc.
- Several applications of AI that have not only improved our day-to-day lives but help in saving lives
- Google Maps
- Web Search
- Intelligent Assistants (Siri, Cortana etc.)
- Targeted advertising
- Diagnosis of diseases
- Autonomous vehicles
- Playing games (Jeopardy, Chess, Go etc.)
- Robots
Subfields of AI
- Planning
- Natural Language Processing
- Learning (Machine Learning)
- Computer Vision
- Robotics
- Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
- Artificial Neural Networks
Knowledge Representation and Reasoning (KRR)
- Techniques to capture knowledge about the world in a form that machines can understand
- A Car is a type of Vehicle
- Car has exactly four wheels
- Car has at least two doors and at most four doors
- Reasoning is the process of deriving new facts (knowledge) based on existing facts
- All birds fly
- Pigeon is a bird
- Can Pigeon fly?
- KRR is the field of AI that helps an agent to use what it knows (background knowledge) to decide what to do
KRR Formalisms
- Different mechanisms to capture knowledge and reason over it
- Frames
- Semantic Nets
- Logic
- First Order Logic
- Description Logics
- Ontologies
- Resource Description Framework (RDF)
Semantic Web
Three Themes
- Building Models
- Describe the world in abstract terms to simplify its understanding
- Computing with Knowledge
- Machines that can do logical deduction/inference from encoded knowledge in order to draw meaningful conclusions
- Exchanging Information
- Transmission of complex information between machines that allows distribution, interlinking, and reconciliation of knowledge
- RSS - some versions of RSS use RDF
Enabling Technologies
- Purpose is to provide structure to the Web and to the data in general
- Move from web of documents to web of data (Linked Data)
- Semantic Web technologies and W3C standards
- RDF (Resource Description Framework)
- OWL (Web Ontology Language)
- SPARQL (query language)
- SHACL (Shapes Constraint Language)
Linked Data
https://lod-cloud.net/
Structured Data (RDF) Demo
RDF Graph, Property Graph, Knowledge Graph
RDF Graph
- Triples that describe any resource
- <Delhi> <capitalOf> <India>
- Triples are directed labelled graphs
Property Graph
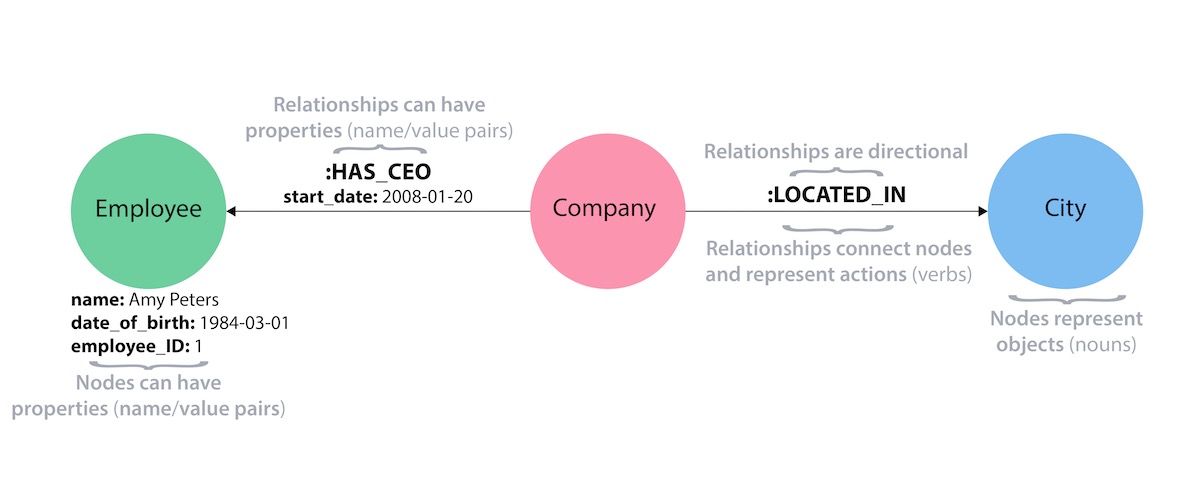
Knowledge Graph
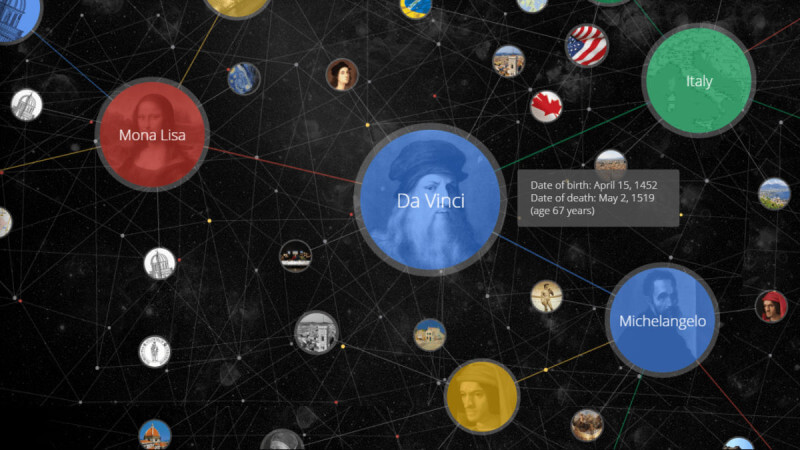
Knowledge Graph
- There is no standard definition of Knowledge Graphs
- It is a graph that captures knowledge in the form of entities, relationships between them, properties, and additional information including provenance
- "Things" not strings. Things should have semantics.
- Eg: What does it mean to be a "Person", "Organization", etc.
- Things are entities that have properties and are connected by relationships
Applications
- Knowledge Graphs are used in several domains and by several commercial enterprises
- Healthcare
- Geoscience
- Industrial domains such as manufacturing, power, oil and gas
- Web Search
- Recommender systems
- Conversational agents (chatbots, QA systems)
- Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Ebay, LinkedIn, GE, Accenture etc.
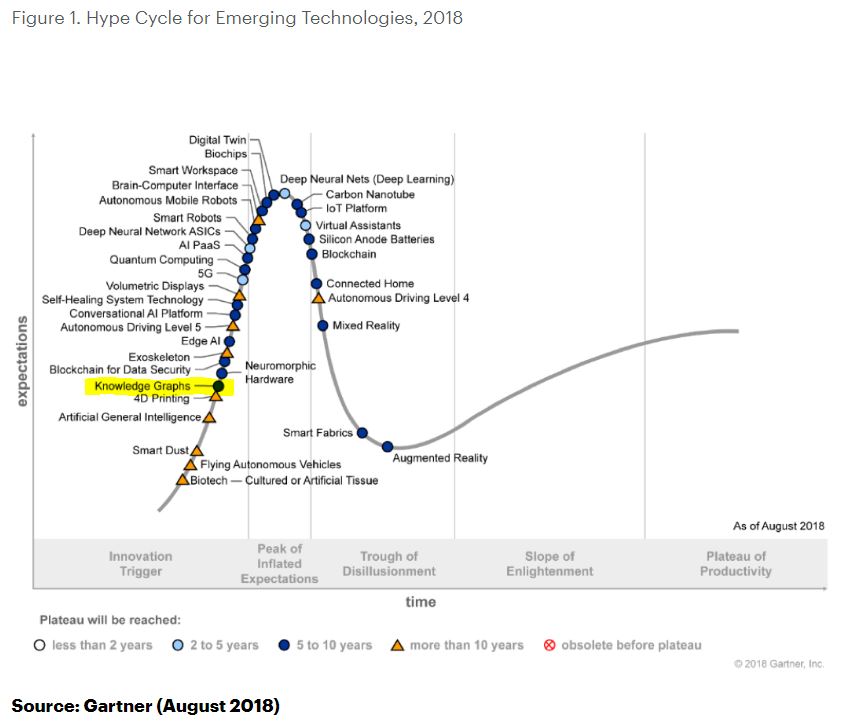
Gartner's Hype Cycle
References
- Textbook: Foundations of Semantic Web Technologies. Pascal Hitzler et. al. CRC Press.
- Reference book: Artificial Intelligence. Stuart Russell, Peter Norvig. Pearson
- Reference book: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning. Ronald Brachman, Hector Levesque. Morgan Kaufmann